First discovered by ProofPoint researchers, Bart ransomware is distributed by the same Russian Cyber Mafia behind Dridex 220 and Locky. Bart doesn't communicate with a command and control (C&C) server, so it can encrypt files without being connected to a computer.
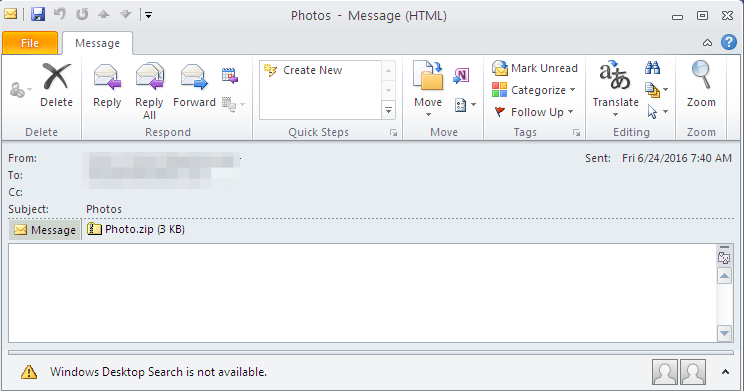
Bart is spread to end users via phishing emails containing .zip attachments with JavaScript Code and use social engineering to trick users into opening the 'photo' attachments. The zipped files are obfuscated to make it more hard to tell what actions they are performing. See screenshot above for an example of what they look like. If opened, these attachments download and install the intermediary loader RockLoader which downloads Bart onto the machine over HTTPS.
Once executed, it will first check the language on the infected computer. If the malware detects Russian, Belorussian, or Ukrainian, the ransomware will terminate and will not proceed with the infection. If it's any other language, it will start scanning the computer for certain file extensions to encrypt.
Because Bart does not require communication with C&C infrastructure prior to encrypting files, Bart could possibly encrypt machines sitting behind corporate firewalls that would otherwise block such traffic. Thus, organizations need to ensure that Bart is blocked at the email gateway using rules that block zipped executables.
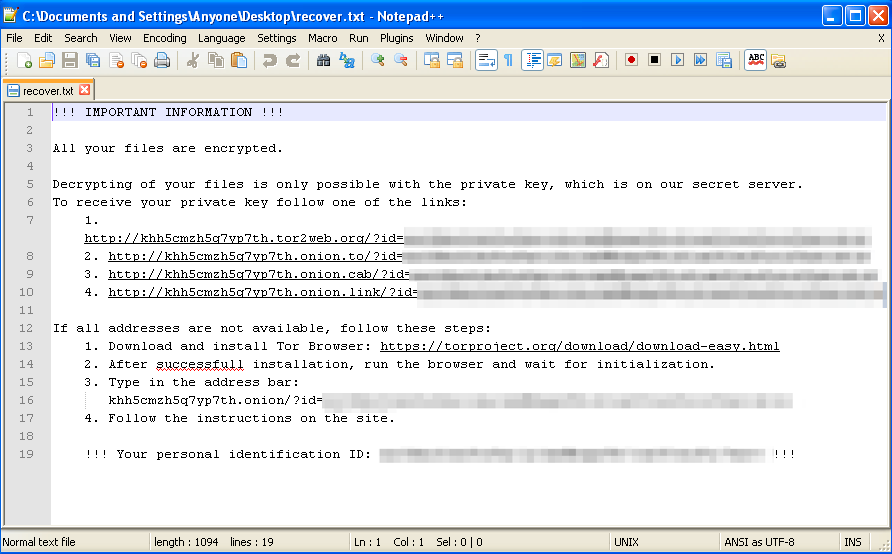
Once it has finished encrypting files, Bart will display a ransom note similar to Locky but with its own unique ransomware code. Current demand is 3 bitcoins (about $2,000) to decrypt the victim's files.
UPDATE: There is a free Bart decryptor available: http://www.avg.com/us-en/ransomware-decryption-tools#bart
